Quick Start Guide
Get your API synchronization up and running with this step-by-step guide.
Configuration Flow
Step 1: Access Configuration
Navigate to Settings → Technical → BJ API → API Configurations in your Odoo interface.
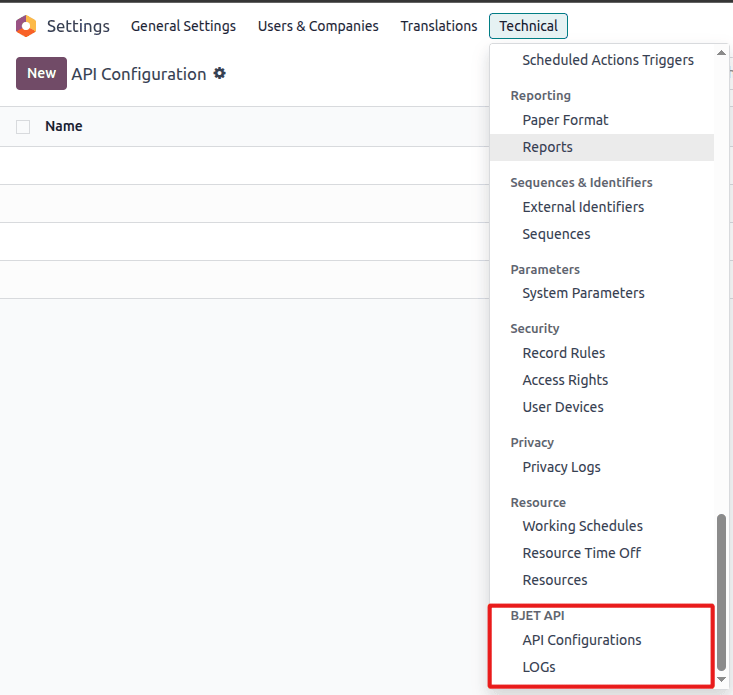 Navigate to Settings → Technical → BJ API → API Configurations
Navigate to Settings → Technical → BJ API → API Configurations
Step 2: Create New Configuration
Click the Create button to start a new API synchronization configuration.
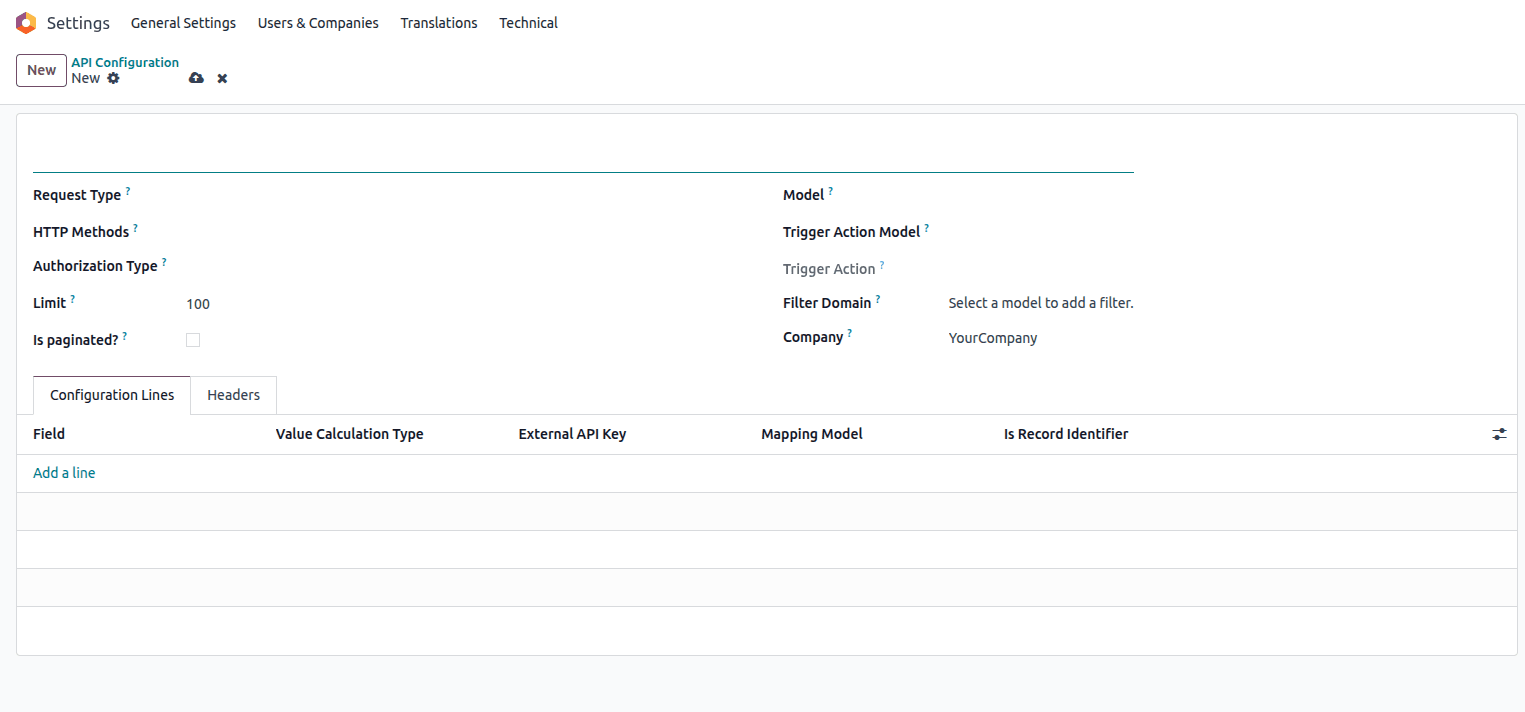 The API Configuration creation form
The API Configuration creation form
Step 3: Choose Configuration Type
Select between Inbound (receiving data) or Outbound (sending data) synchronization:
Inbound Configuration
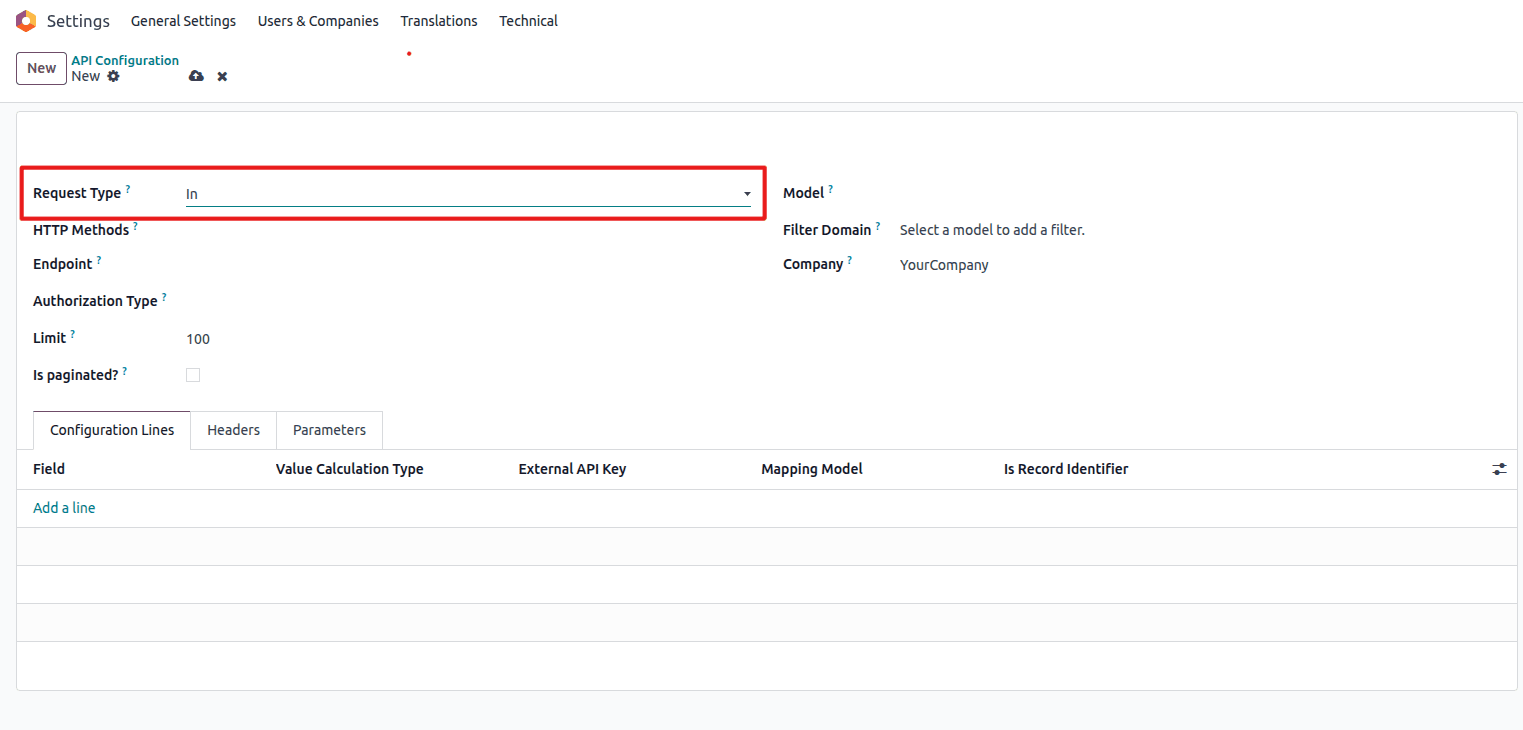 Select "In" for receiving data from external systems
Select "In" for receiving data from external systems
- Purpose: For inbound data (from an external system to Odoo)
- Example:
GET /bj_api_sync/v1/partners
Outbound Configuration
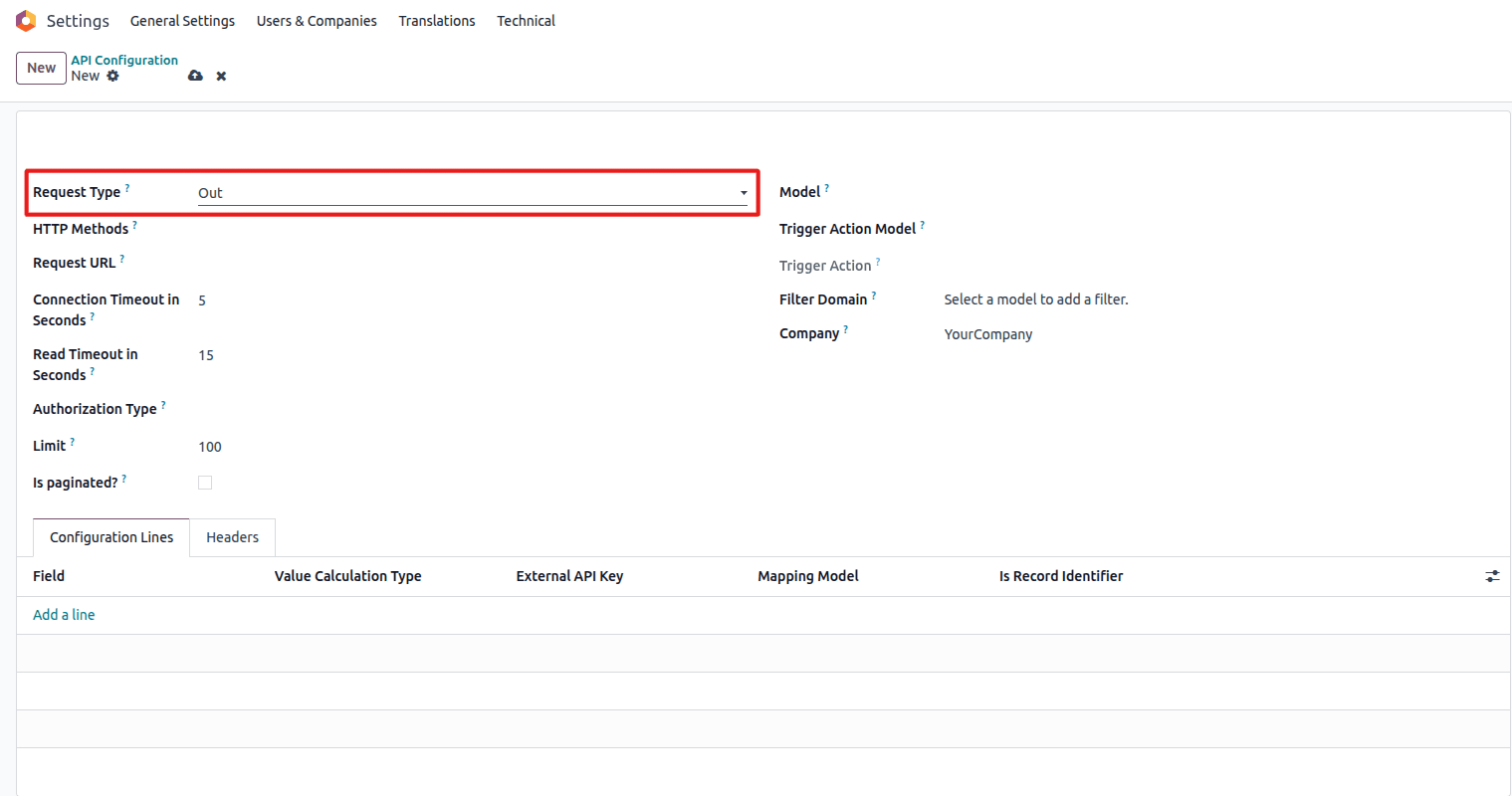 Select "Out" for sending data to external systems
Select "Out" for sending data to external systems
- Purpose: For outbound data (from Odoo to an external system)
- Example:
config._make_outbound_http_request(record, config_id_ref, timeout=60)
Step 4: Configure Basic Settings
General Configuration
- Name – a descriptive name for the configuration
- Model – the Odoo model to be synchronized
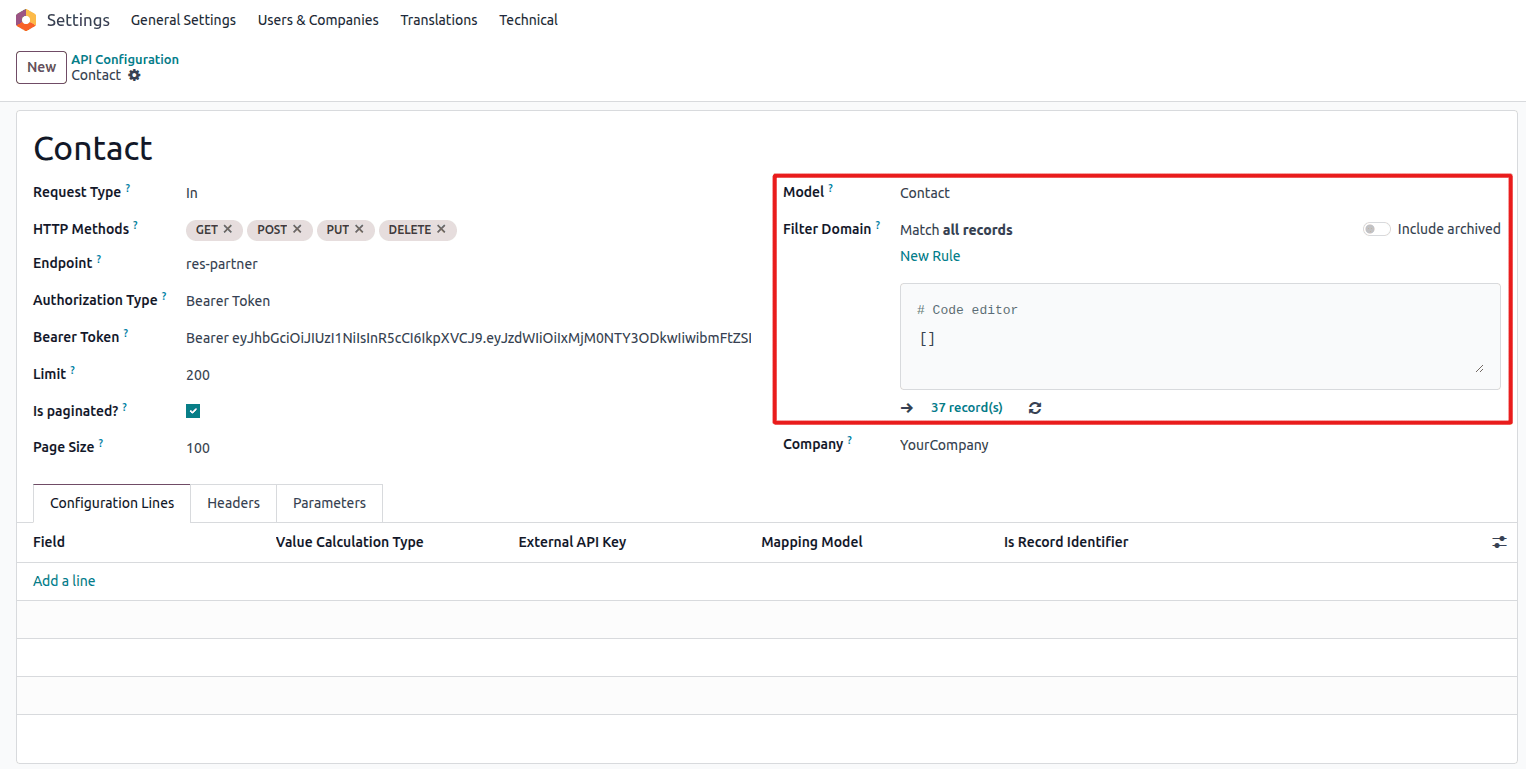 Select target model and filter settings
Select target model and filter settings
API Settings
- Endpoint / URL – specify the API endpoint or external URL
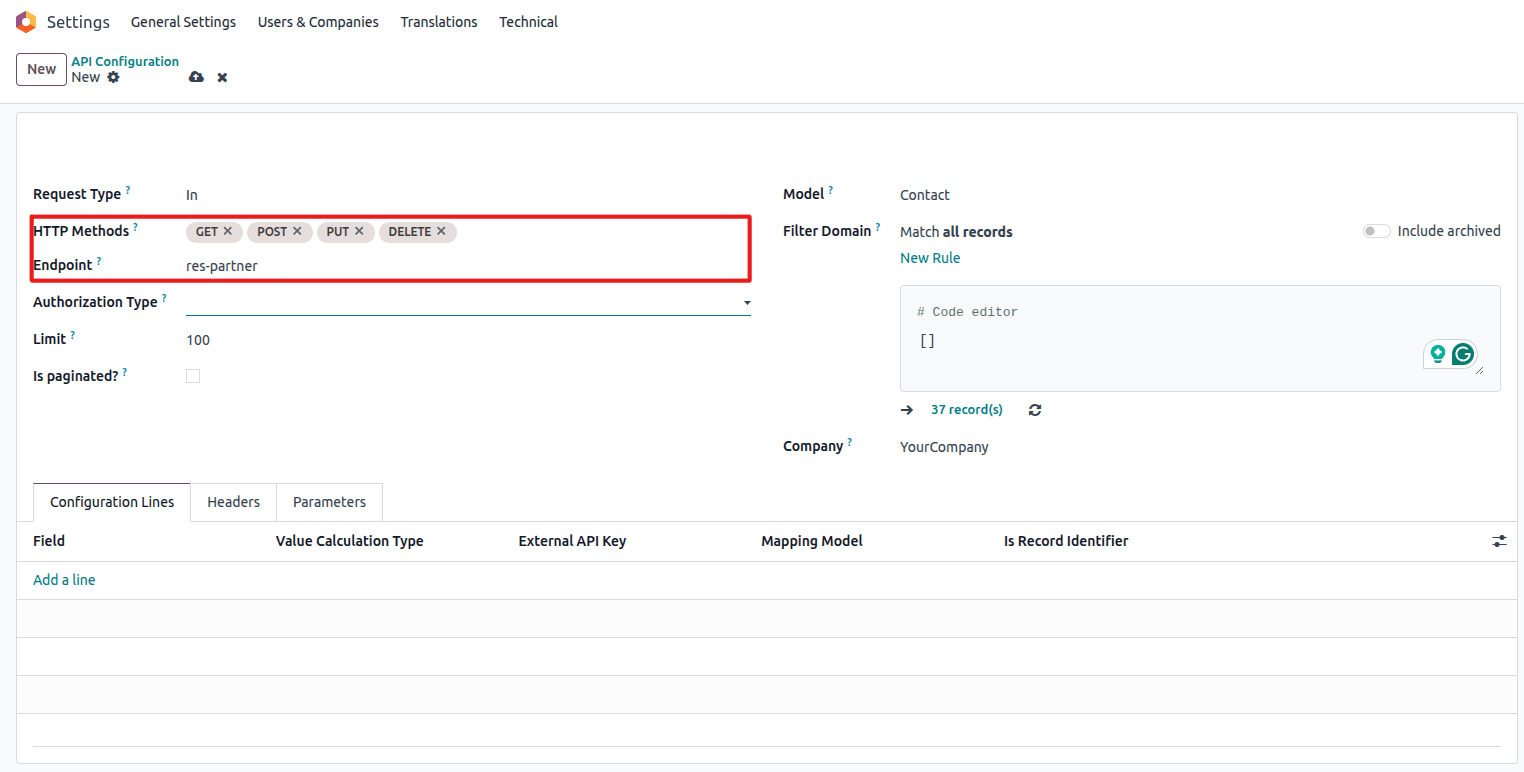 Configure API endpoint
Configure API endpoint
- HTTP Methods – select the allowed HTTP operations
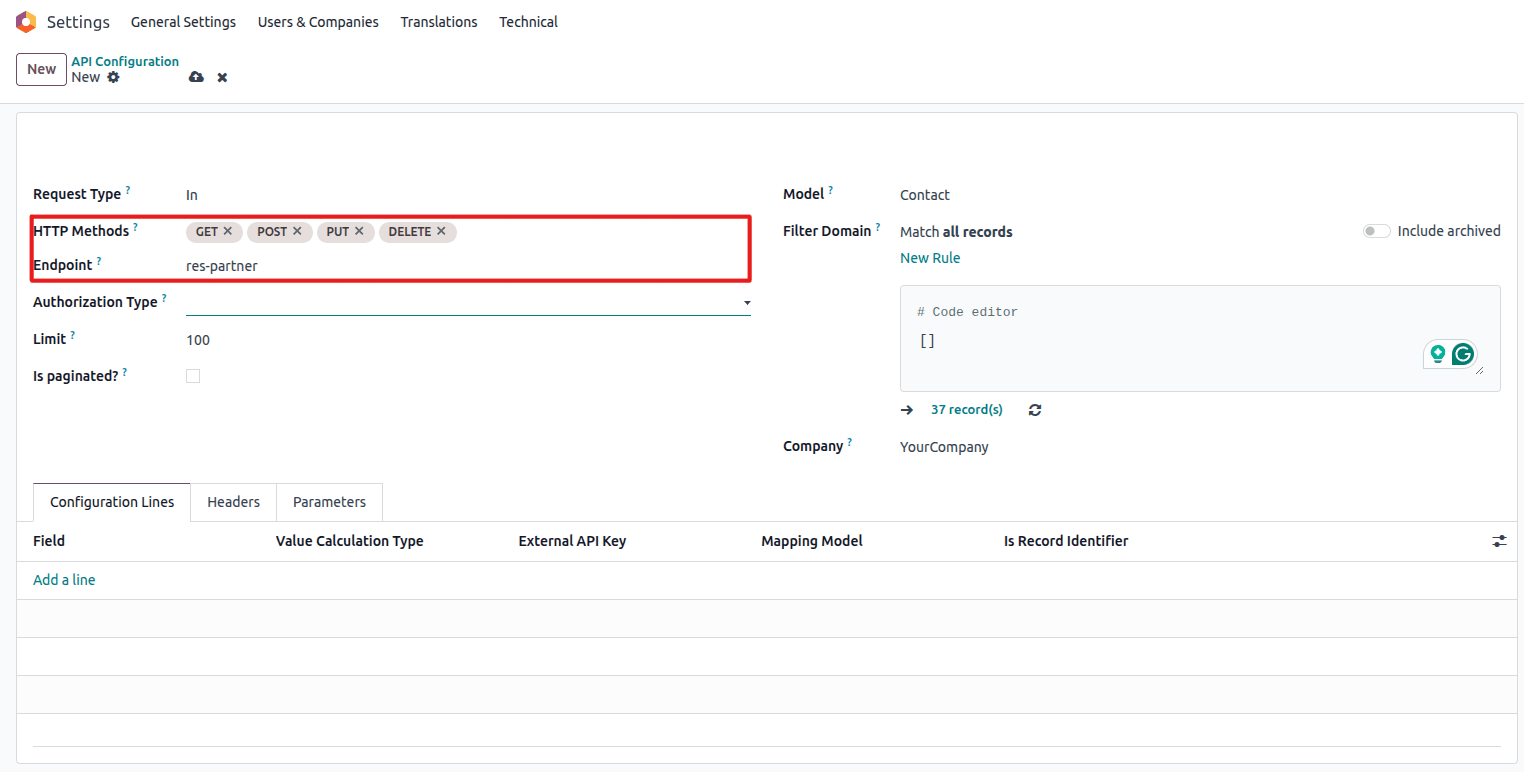 Select allowed HTTP methods
Select allowed HTTP methods
- Authentication – configure the required security settings
Authentication Types
- No Auth – no authentication required
- Basic Auth – authenticate with login and password
- Bearer Token – authenticate with a bearer token
Step 5: Set Up Field Mappings
Define how Odoo fields correspond to external API data keys in the Configuration Lines section:
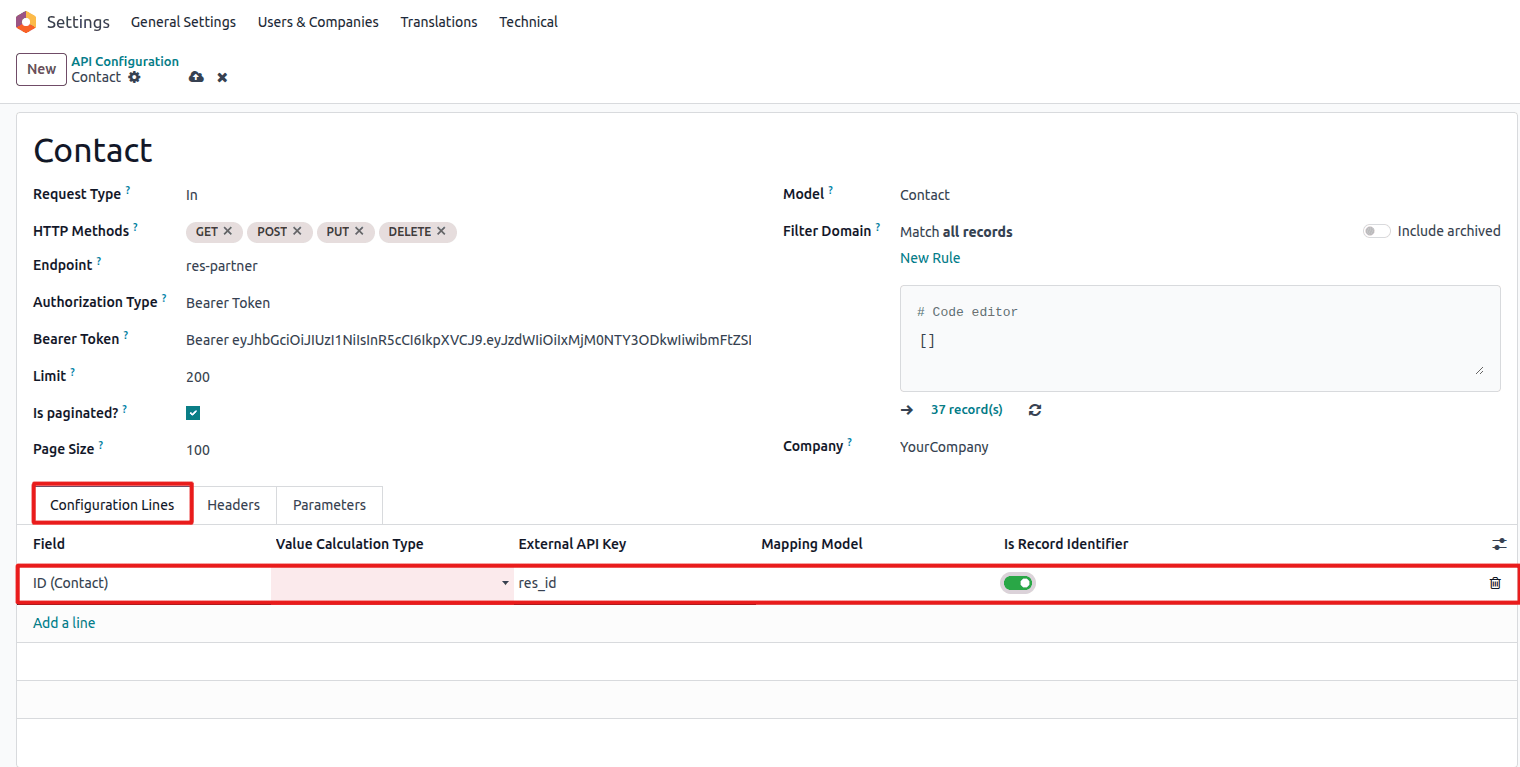 Configure field mappings between Odoo and external API
Configure field mappings between Odoo and external API
- Click Add a line in the Configuration Lines section
- Select the Field (Odoo field to be mapped)
- Enter the External API Key (corresponding key in the external API)
- Mark one field as Record Identifier (exactly one per configuration)
Value Calculation Types
- Plain – direct mapping between an Odoo field and the external API key
- Relational with Mapping Model – for relational fields (Many2one, One2many, Many2many)
- Python Script for Plain Value – calculate the value for a simple field using a Python script
- Relational with Python Script – process data for a relational field using a Python script
Step 6: Test and Deploy
Save the configuration and run sample API requests to verify functionality before deployment.