Inbound API Configuration
Configure Odoo to receive data from external systems through RESTful API endpoints.
Step-by-Step Configuration
Step 1: Access Configuration
Navigate to Settings > Technical > BJ API > API Configurations in your Odoo interface.
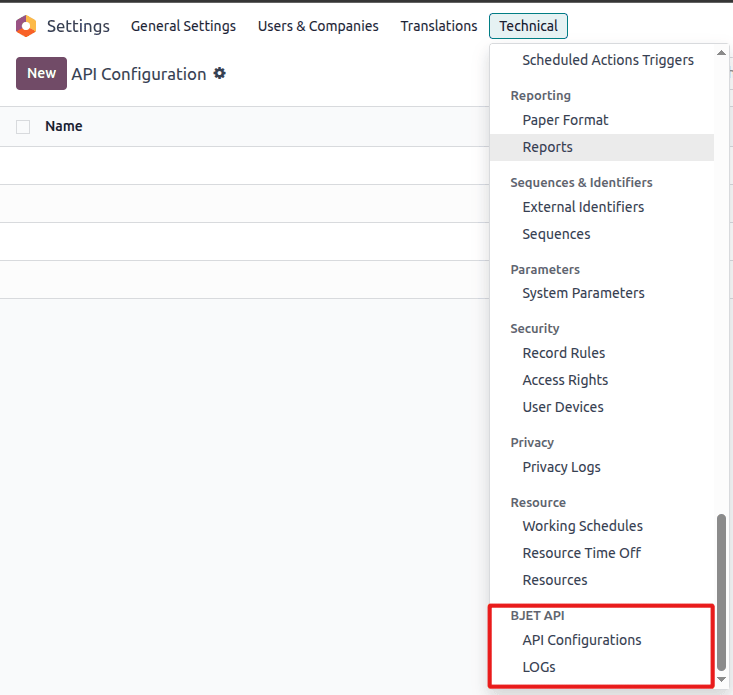 API Configurations menu in Technical Settings
API Configurations menu in Technical Settings
Step 2: Create New Configuration
Click the Create button to start a new API synchronization configuration.
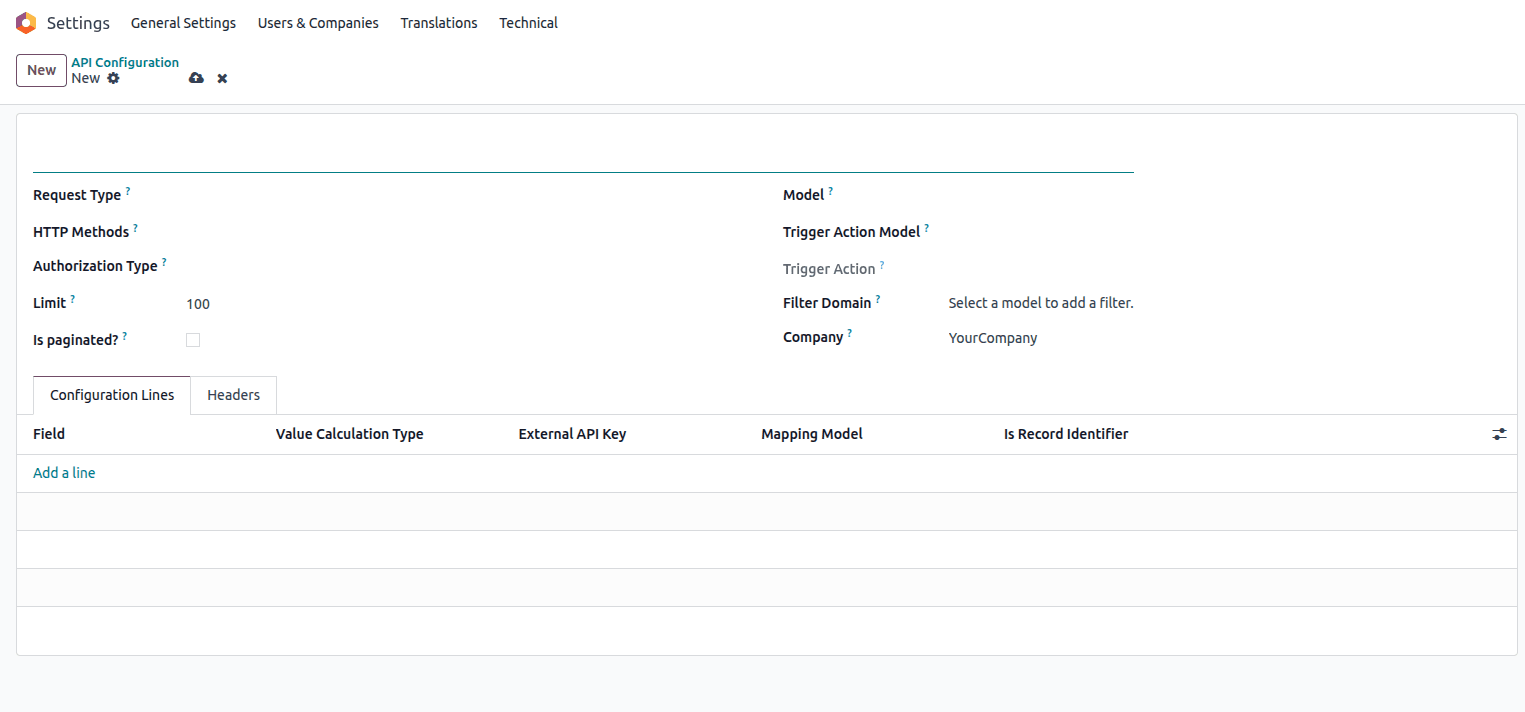 New API Configuration form
New API Configuration form
Step 3: Set Request Type
Select Request Type as "In" for inbound data synchronization.
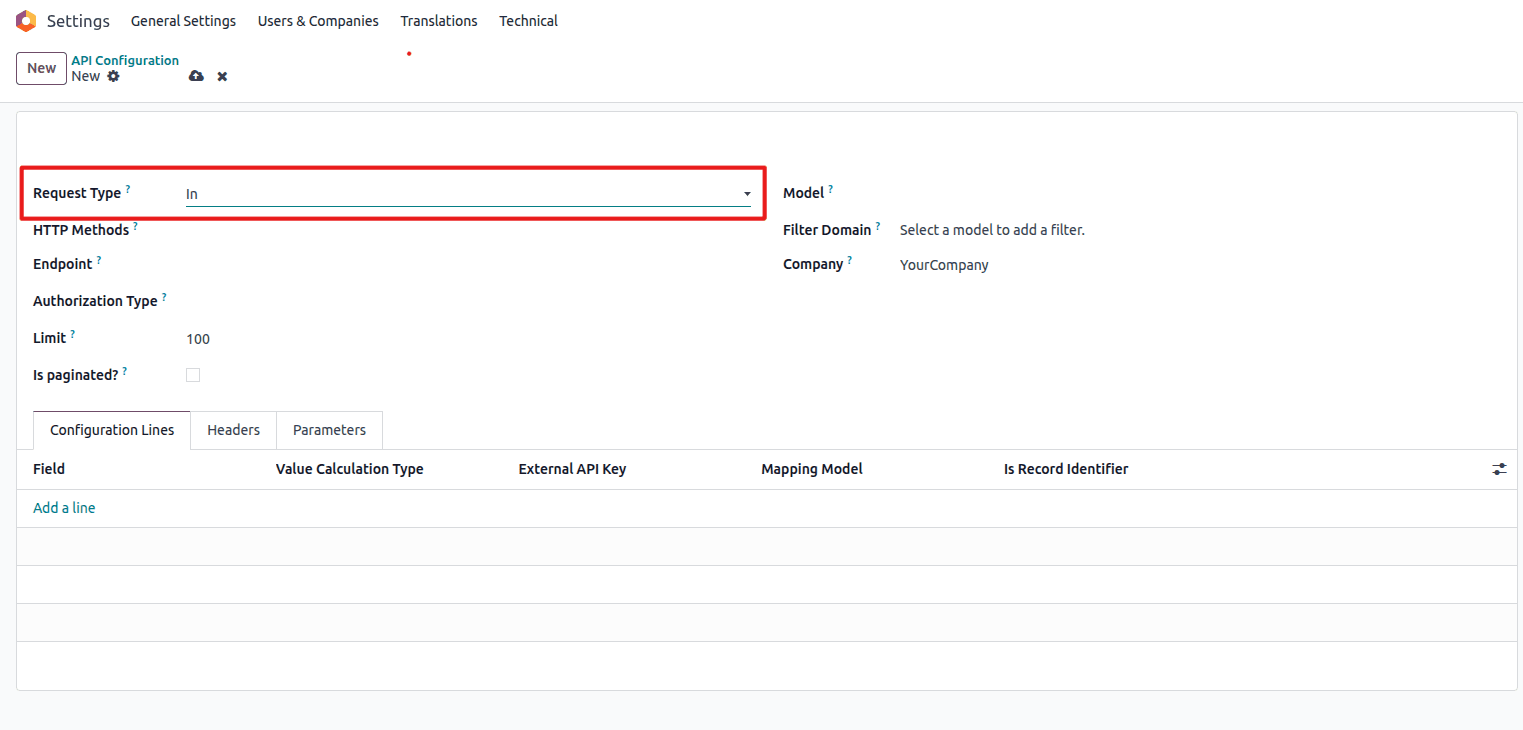 Select "In" for inbound data synchronization
Select "In" for inbound data synchronization
Step 4: Configure Basic Settings
General Settings
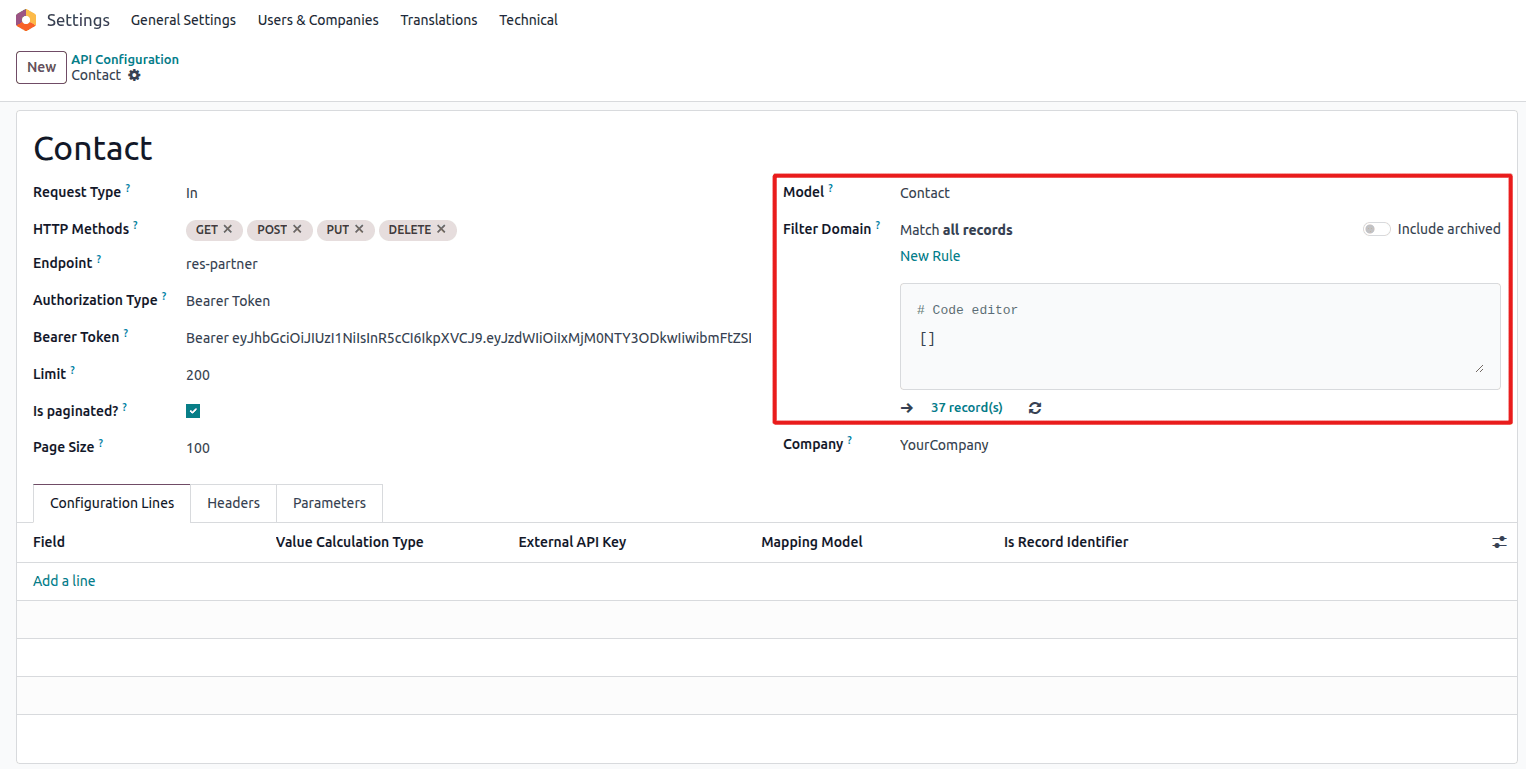 Configure model and filter settings
Configure model and filter settings
- Name: Enter a descriptive name (e.g., "Partner Import API")
- Model: Select the target Odoo model (e.g.,
res.partner,product.product) - Filter Domain: Add conditions to filter records (optional)
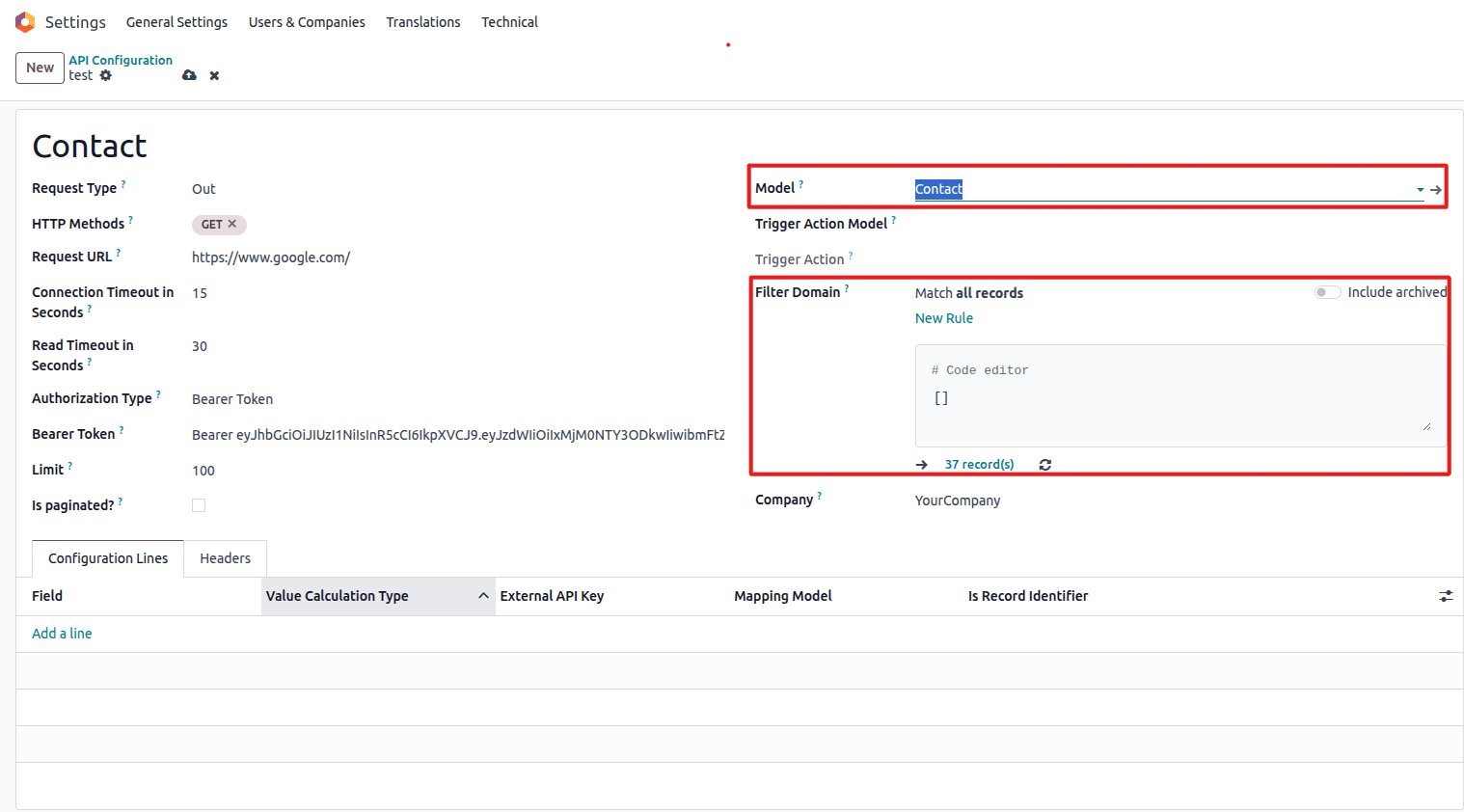 Set up domain filters for record selection
Set up domain filters for record selection
[('active', '=', True)]
Endpoint Configuration
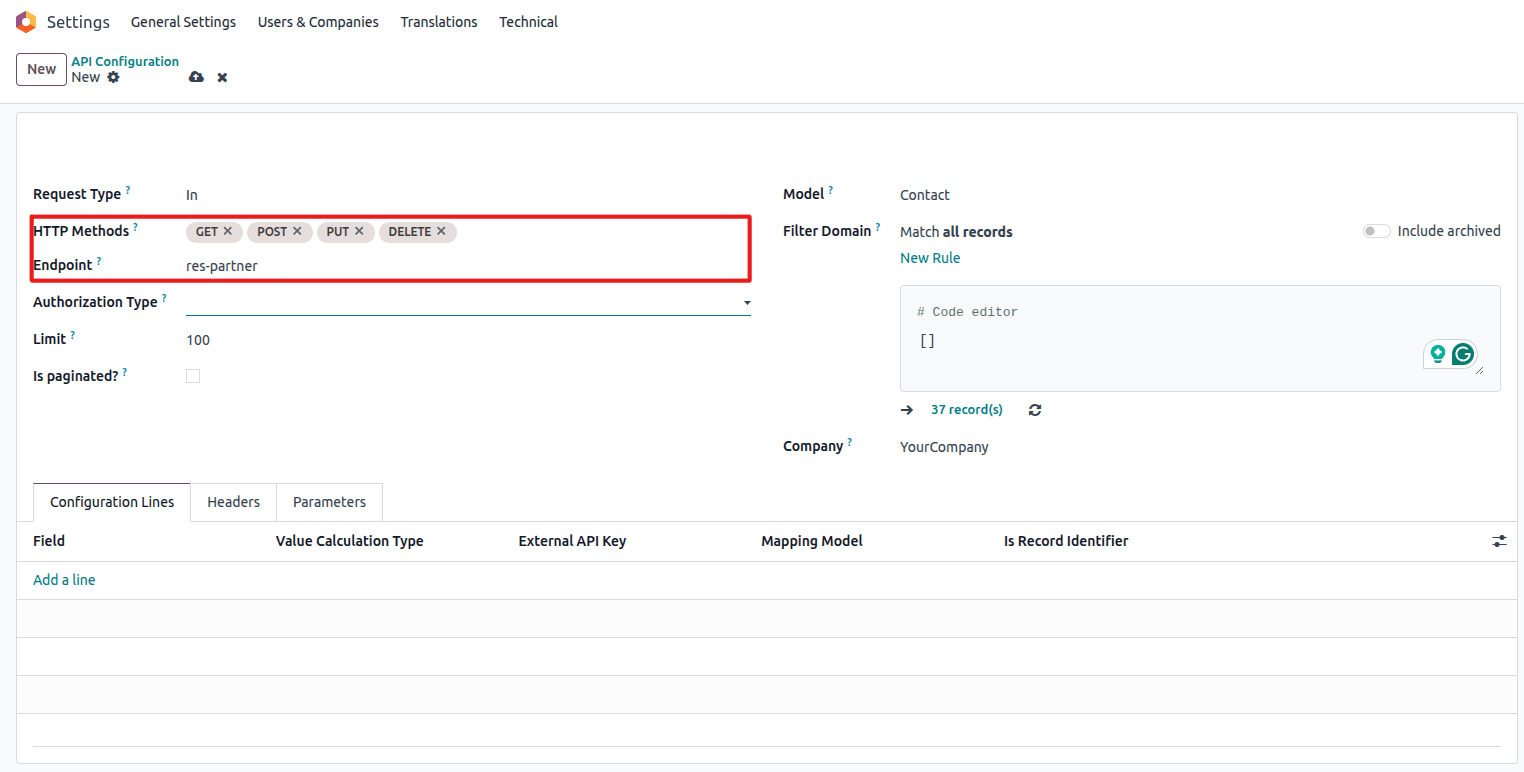 Configure the API endpoint identifier
Configure the API endpoint identifier
- Endpoint: Define a unique identifier for your endpoint (e.g., "partners")
- This creates the API path:
/bj_api_sync/v1/partners
HTTP Methods
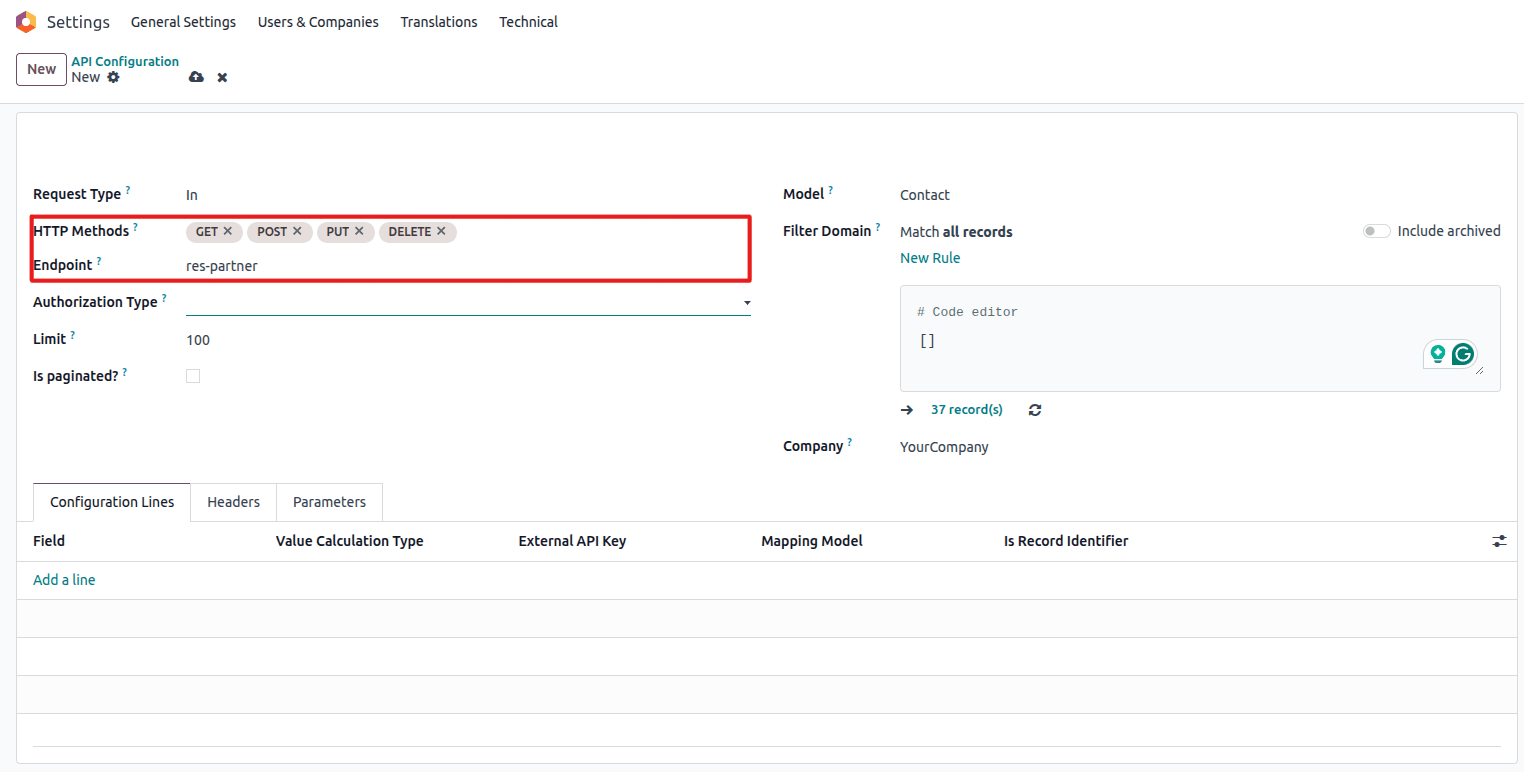 Select allowed HTTP operations
Select allowed HTTP operations
Select the allowed operations:
- GET: Retrieve records
- POST: Create new records
- PUT: Update existing records
- DELETE: Remove records
Step 5: Configure Authentication
Choose your authentication method:
No Authentication
Suitable for internal or public APIs with no security requirements.
Basic Authentication
Requires username and password:
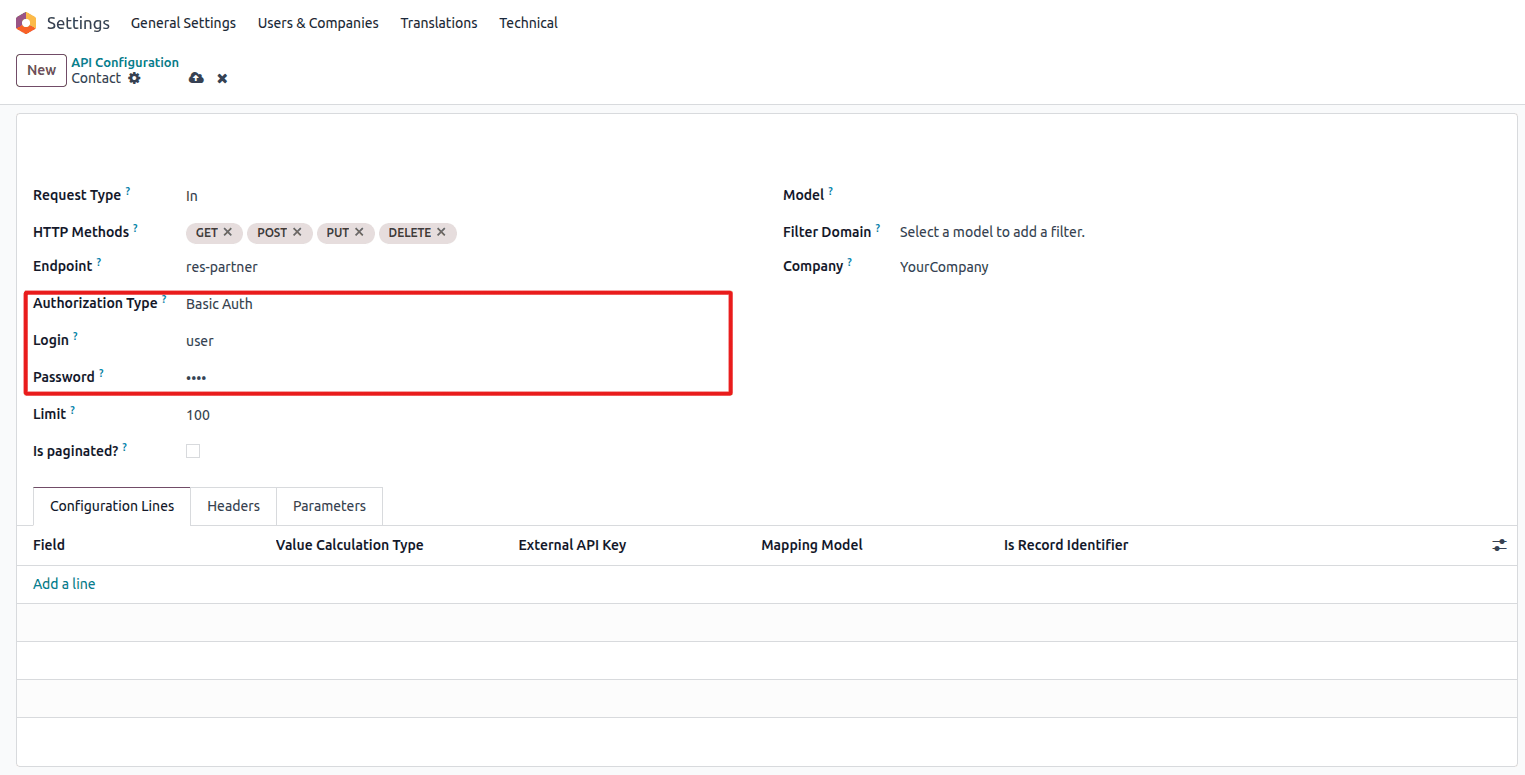 Basic Authentication configuration
Basic Authentication configuration
- Login: API username
- Password: API password
Bearer Token
Uses API key authentication:
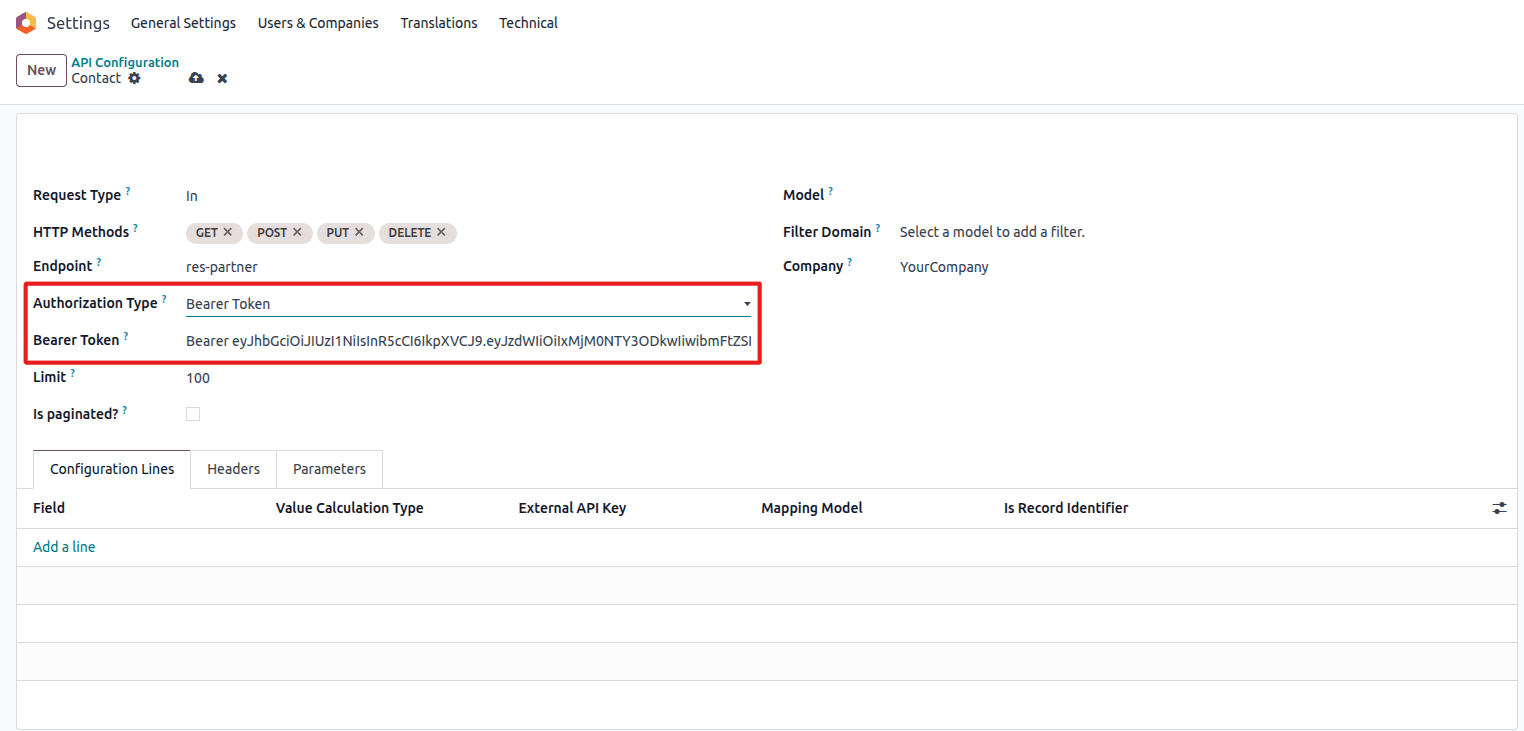 Bearer Token configuration
Bearer Token configuration
- Bearer Token: Your API key or access token
Example header:
Authorization: Bearer your_token_here
Step 6: Set Up Field Mappings
Create Configuration Lines to map Odoo fields to API keys:
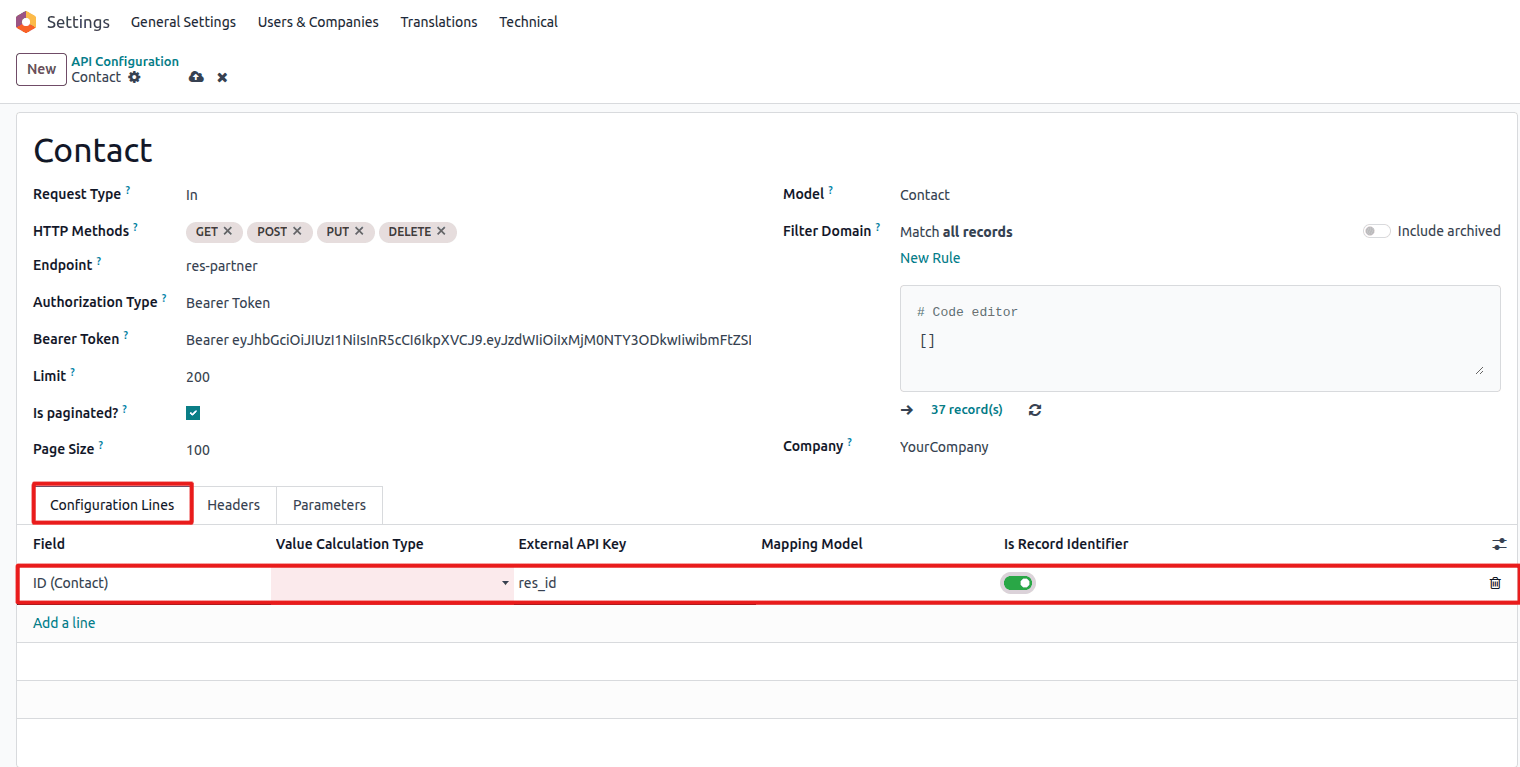 Configure field mappings between Odoo and external API
Configure field mappings between Odoo and external API
| Odoo Field | External API Key | Record Identifier | Value Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | name | ❌ | Plain |
| email_address | ❌ | Plain | |
| ref | customer_id | ✅ | Plain |
| phone | contact_phone | ❌ | Plain |
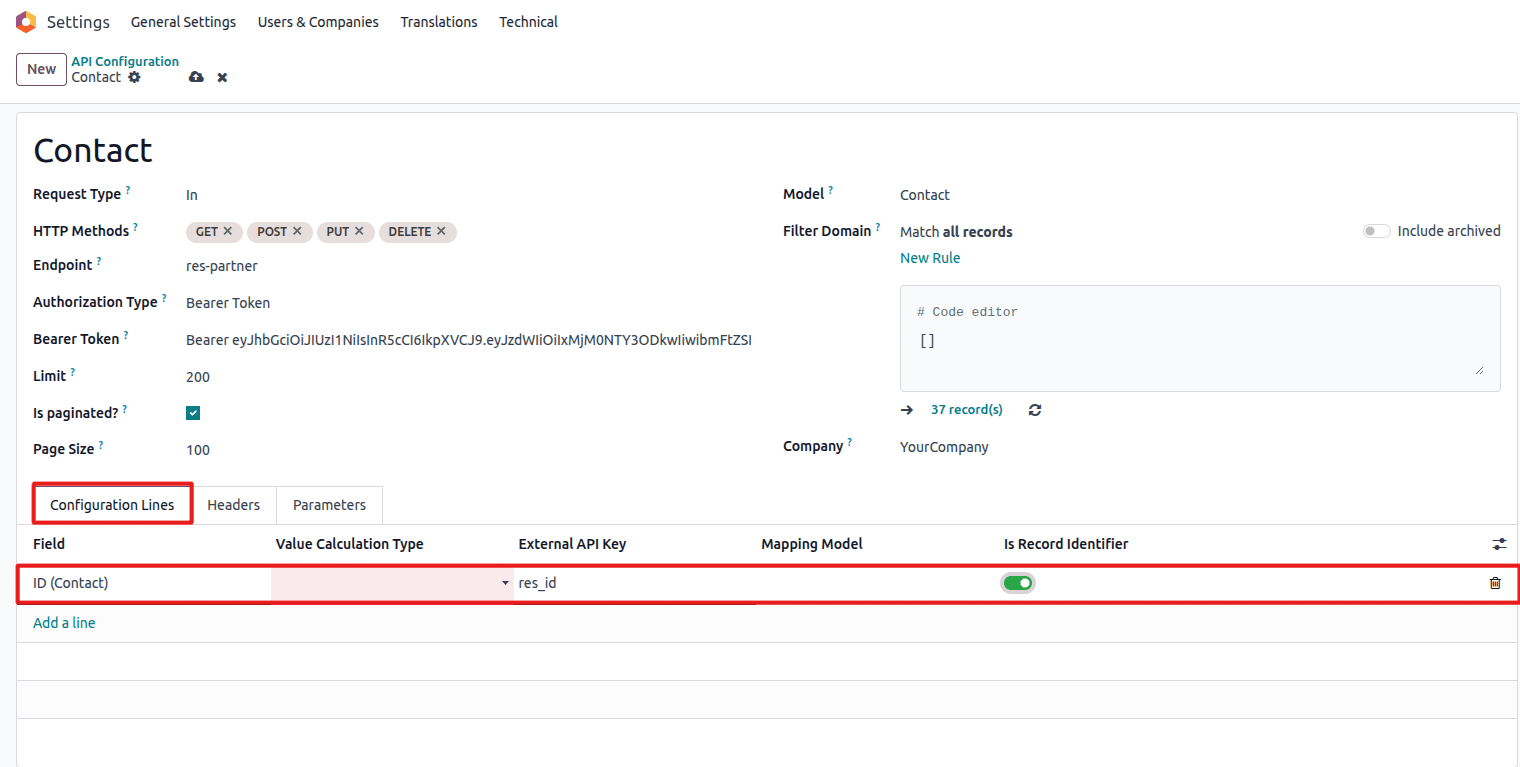 Detailed view of configuration lines with all options
Detailed view of configuration lines with all options
Important: Exactly one field must be marked as the Record Identifier.
Step 7: Configure Pagination (Optional)
For large datasets:
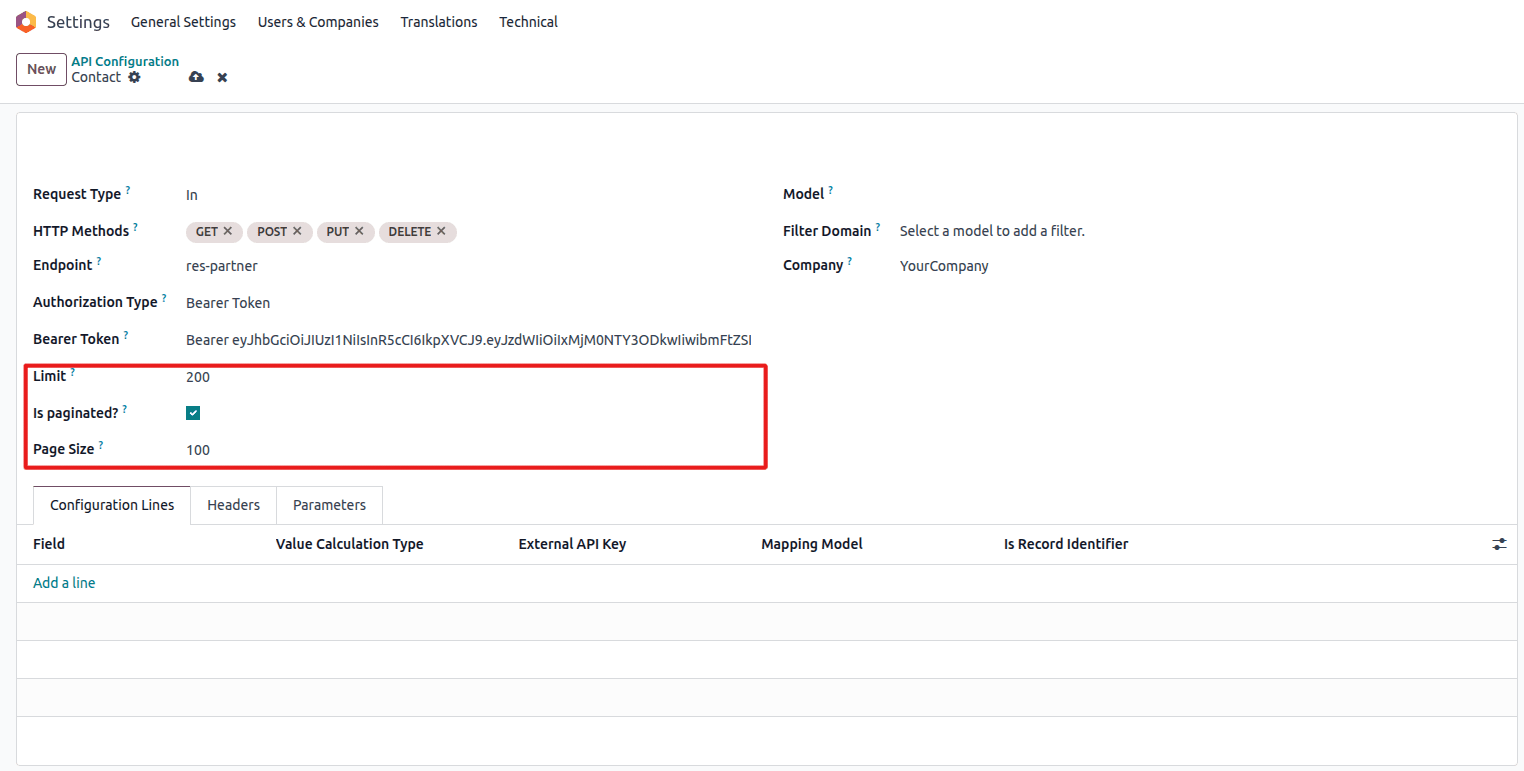 Pagination configuration for large datasets
Pagination configuration for large datasets
- Is Paginated: Enable pagination
- Page Size: Records per request (default: 100)
API Endpoint Patterns
Once configured, your endpoint will be available at:
Base Pattern:
/bj_api_sync/v1/<endpoint_name>
/bj_api_sync/v1/<endpoint_name>/<record_id>
Example Requests
GET Request - Retrieve All Records
curl -X GET "http://localhost:8069/bj_api_sync/v1/partners" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer your_token_here"
GET Request - Retrieve Single Record
curl -X GET "http://localhost:8069/bj_api_sync/v1/partners/123" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer your_token_here"
POST Request - Create New Record
curl -X POST "http://localhost:8069/bj_api_sync/v1/partners" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer your_token_here" \
-d '{
"name": "Test Partner",
"email": "test@example.com",
"phone": "+1234567890"
}'
PUT Request - Update Record
curl -X PUT "http://localhost:8069/bj_api_sync/v1/partners/123" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer your_token_here" \
-d '{
"name": "Updated Partner Name",
"email": "updated@example.com"
}'
DELETE Request - Remove Record
curl -X DELETE "http://localhost:8069/bj_api_sync/v1/partners/123" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer your_token_here"
Processing Pipeline
The inbound request follows this flow:
HTTP Request → Authentication → Method Check → Configuration Lookup
→ Data Transformation → Record Processing → Response Generation → Logging
Response Formats
Success Response
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"id": 123,
"name": "Test Partner",
"email": "test@example.com"
}
}
Error Response
{
"status": "error",
"message": "Authentication failed",
"code": 401
}
Common Error Codes
| Code | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| 401 | Unauthorized | Check authentication credentials |
| 404 | Not Found | Verify endpoint configuration |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed | Enable the HTTP method in configuration |
| 400 | Bad Request | Validate JSON data format |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | Check server logs for details |
Best Practices
- Use HTTPS in production environments
- Implement rate limiting to prevent abuse
- Validate input data using Python scripts
- Log all requests for audit trail
- Test thoroughly before production deployment